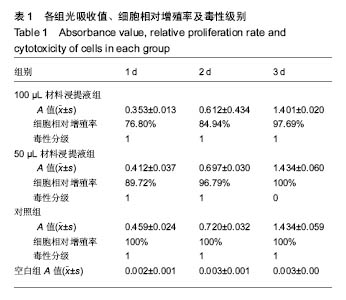
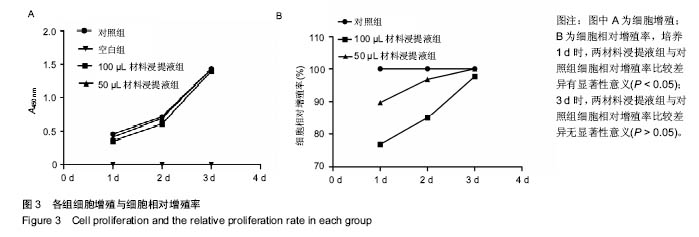
| [1]韩德民.鼻内窥镜外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2001.[2]Massey CJ,Suh JD,Tessema B,et al.Biomaterials in Rhinology.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2016;154(4):606-617.[3]Valentine R,Wormald PJ,Sindwani R.Advances in absorbable biomaterials and nasal packing.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2009;42(5):813-828.[4]Jeong HS,Lee HK,Kim HS,et al.A case-controlled, retrospective, comparative study on the use of biodegradable synthetic polyurethane foam versus polyvinyl acetate sponge after nasal fracture reduction.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2014; 43(6):717-721.[5]李芳霞.聚氨酯—明胶/壳聚糖复合材料的制备及性能研究[D].西南交通大学,2014:72.[6]陈寅生,侯春林,魏长征,等.羟丁基壳聚糖的生物相容性研究[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2015,12(3):14-17,81.[7]雷智坚.聚乙烯醇/羟基磷灰石复合水凝胶修复膝关节软骨缺损的组织相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(30): 4832-4836. [8]周慧通,方大为,王波,等.冷冻干燥法制备CS/AMPS/PEGDA光交联多孔水凝胶及其性能[J].材料科学与工程学报,2015, 33(3): 432-437,441.[9]ISO 10993-5-2009医疗器械的生物学评价.第5部分:体外细胞毒性试验.[10]李双奎.壳聚糖类鼻腔填塞止血材料的研究与制备[D].北京化工大学,2015:70.[11]张晓丹.壳聚糖衍生物和聚乙二醇双丙烯酸酯混合材料的制备及其性能表征[D].北京化工大学,2009:67.[12]吴邦耀,罗卓荆,孟浩,等.胶原-明胶支架材料交联改性的制备及细胞毒性实验研究[J].生物医学工程与临床,2007,11(6): 420-425.[13]初晓夏,王斌,王海涛,等.海藻酸钙止血敷料与临床常用3种止血敷料体外细胞毒性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(43): 6998-7003.[14]Weber RK.Nasal packing and stenting. Laryngorhinootologie. 2009;88 Suppl 1: S139-55.[15]Kim YS,Kim YH,Kim NH,et al.A prospective, randomized, single-blinded controlled trial on biodegradable synthetic polyurethane foam as a packing material after septoplasty.Am J Rhinol Allergy.2011;25(2):e77-79.[16]Verim A,Seneldir L,Naibo?lu B,et al.Role of nasal packing in surgical outcome for chronic rhinosinusitis with polyposis. Laryngoscope.2014;124(7):1529-1535.[17]Moon SH,Baek SO,Jung SN,et al.Efficacy of biodegradable synthetic polyurethane foam for packing nasal bone fractures. J Craniofac Surg.2012;23(6):1848-1850.[18]Wang TC,Tai CJ,Tsou YA,et al.Absorbable and nonabsorbable packing after functional endoscopic sinus surgery: systematic review and meta-analysis of outcomes. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.2015;272(8):1825-1831.[19]张永杰,王彤,臧洪瑞.鼻腔硅胶扩张引流管临床应用观察[J].中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2010,58(7):385-386.[20]吴曙霞,刘伟,李玉霞,等.关于我国健康产业的概念内涵与发展前景的思考[J].中华健康管理学杂志,2015,9(5):390-392.[21]谢阳江,陈恩涛,吴波,等.生物可吸收材料在关节骨折内固定中的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(34):5076-5081.[22]林红赛,王春仁,王志杰,等.生物材料的细胞生物相容性评价方法的研究进展[J].中国医疗[23]吴邦耀.新型组织工程神经支架材料的生物安全性评价[D].第四军医大学,2008:66.[24]邹颖,王文梅,朱雅男,等.CCK-8法评价口腔粘结材料的体外细胞毒性研究[J].口腔医学研究,2011,27(8):673-675.[25]谭帼馨,王迎军,关燕霞.聚乙二醇双丙烯酸酯的紫外光聚合[J].高分子材料科学与工程, 2008,24(10):33-36.[26]侯丹丹,郝彤,叶霖,等.通过麦克加成反应形成的三臂聚乙二醇丙烯酸酯可注射水凝胶的制备与表征[J].高分子学报,2008,1(4): 388-393.[27]侯立刚,杨建义.骨修复中应用的生物降解可吸收材料[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(3):441-445.[28]刘水莲,周洋,陈福花,等.新型羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶流变性能,药物释放及细胞相容性研究[J].化学学报,2015,73(1):47-52.[29]饶思奇.壳聚糖/聚乙烯醇水凝胶的制备及其性能研究[D].湖北大学,2014:66.[30]Zeng T,Zhang Y,Yan Q,et al.Construction and in vitro evaluation of enzyme nanoreactors based on carboxymethyl chitosan for arginine deprivation in cancer therapy.Carbohydr Polym.2017;162:35-41. [31]Jena SK,Samal SK,Kaur S,et al.Potential of amphiphilic graft copolymer α-tocopherol succinate-g-carboxymethyl chitosan in modulating the permeability and anticancer efficacy of tamoxifen.Eur J Pharm Sci.2017;101:149-159.[32]Vo DT,Sabrina S,Lee CK.Silver deposited carboxymethyl chitosan-grafted magnetic nanoparticles as dual action deliverable antimicrobial materials.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;73:544-551.[33]Ni S,Xie Y,Tang Y,et al.Nebulized anionic guanidinylated O-carboxymethyl chitosan/N-2-hydroxypropyltimehyl ammonium chloride chitosan nanoparticles for siRNA pulmonary delivery: preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation.J Drug Target. 2017:1-12.[34]Wang X,Wei B,Cheng X,et al.3-Carboxyphenylboronic acid-modified carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles for improved tumor targeting and inhibitory.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017.pii:S0939-6411(16)30265-X.doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.12.034.[Epub ahead of print][35]Tu L,Wang M,Zhao WY,et al.miRNA-218-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan - Tocopherol nanoparticle to suppress the proliferation of gastrointestinal stromal tumor growth. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;72:177-184.[36]Jena SK,Sangamwar AT.Corrigendum to "Polymeric micelles of amphiphilic graft copolymer of a-tocopherol succinate-g-carboxymethyl chitosan for tamoxifen delivery: Synthesis, characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetic study" [Carbohydr. Polym. 151 (2016) 1162-1174].Carbohydr Polym.2017;157:904. [37]Song L,Li L,He T,et al.Peritoneal adhesion prevention with a biodegradable and injectable N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan-aldehyde hyaluronic acid hydrogel in a rat repeated-injury model.Sci Rep.2016;6:37600. [38]Wongkom L,Jimtaisong A.Novel biocomposite of carboxymethyl chitosan and pineapple peel carboxymethylcellulose as sunscreen carrier.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;95:873-880.[39]Yu S,Zhang X,Tan G,et al.A novel pH-induced thermosensitive hydrogel composed of carboxymethyl chitosan and poloxamer cross-linked by glutaraldehyde for ophthalmic drug delivery.Carbohydr Polym.2017;155:208-217. [40]Lin Q,Huo Q,Qin Y,et al.Development of ligustrazine hydrochloride carboxymethyl chitosan and collagen microspheres: Formulation optimization, characterization, and vitro release.Bioengineered.2017;8(1):55-60. |
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)